Tiny baby fleas may seem harmless, but they can quickly escalate into a full-blown infestation if left unchecked. These minuscule creatures are the early stage of fleas, which can cause significant discomfort for both pets and humans. Understanding their lifecycle and behavior is crucial in preventing and controlling infestations.
As a pet owner or someone dealing with flea-related issues, it's essential to recognize the signs of tiny baby fleas. Early detection can save you from dealing with a much larger problem later. This article will delve deep into the world of flea larvae, their lifecycle, and effective strategies to combat them.
Whether you're looking to protect your furry friends or safeguard your home, this guide provides comprehensive insights into tiny baby fleas. From identifying them to understanding their behavior and implementing preventive measures, we'll cover everything you need to know.
Read also:No Lube No Protection Copy Paste
Table of Contents
- Understanding Tiny Baby Fleas
- Lifecycle of Fleas
- How to Identify Tiny Baby Fleas
- Impact of Tiny Baby Fleas
- Preventing Tiny Baby Fleas
- Treatment Options
- Environmental Control
- Protecting Your Pets
- Protecting Your Home
- Conclusion
Understanding Tiny Baby Fleas
What Are Tiny Baby Fleas?
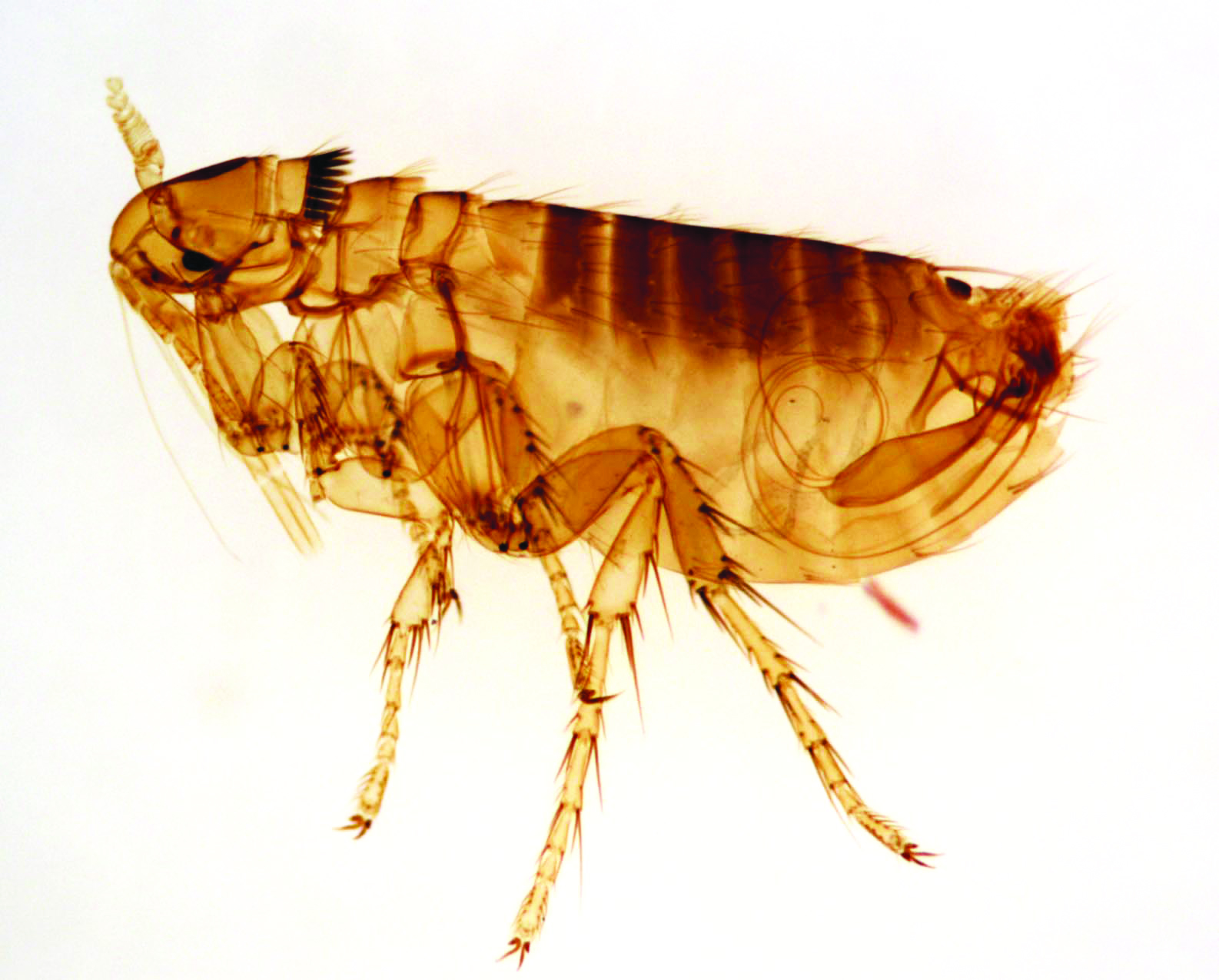
Tiny baby fleas, also known as flea larvae, are the immature stage of fleas in their lifecycle. These larvae are typically about 2-5 millimeters in length and appear as small, white, worm-like creatures. They are often found in areas where adult fleas have laid their eggs, such as carpets, pet bedding, and furniture.
Despite their small size, flea larvae are voracious eaters. They feed on organic debris, flea dirt (feces of adult fleas), and other particles found in their environment. Understanding their behavior and habitat is key to controlling their population.
Lifecycle of Fleas
The lifecycle of fleas consists of four main stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Each stage plays a crucial role in the development of fleas, and targeting specific stages can help in effective flea control.
Egg Stage
Adult female fleas lay eggs after feeding on a host. These eggs are tiny, white, and oval-shaped. They can fall off the host and spread to various areas of your home.
Larval Stage
After hatching from the eggs, flea larvae emerge. This stage lasts about 5-11 days, during which the larvae feed and grow. They are highly sensitive to light and prefer dark, moist environments.
Pupal Stage
Once the larvae have matured, they spin a cocoon to enter the pupal stage. This protective casing shields them from external threats and allows them to develop into adult fleas.
Read also:Cloth Of Io
Adult Stage
Adult fleas emerge from the pupal stage and immediately seek a host for blood meals. They are capable of jumping long distances and can quickly spread infestations.
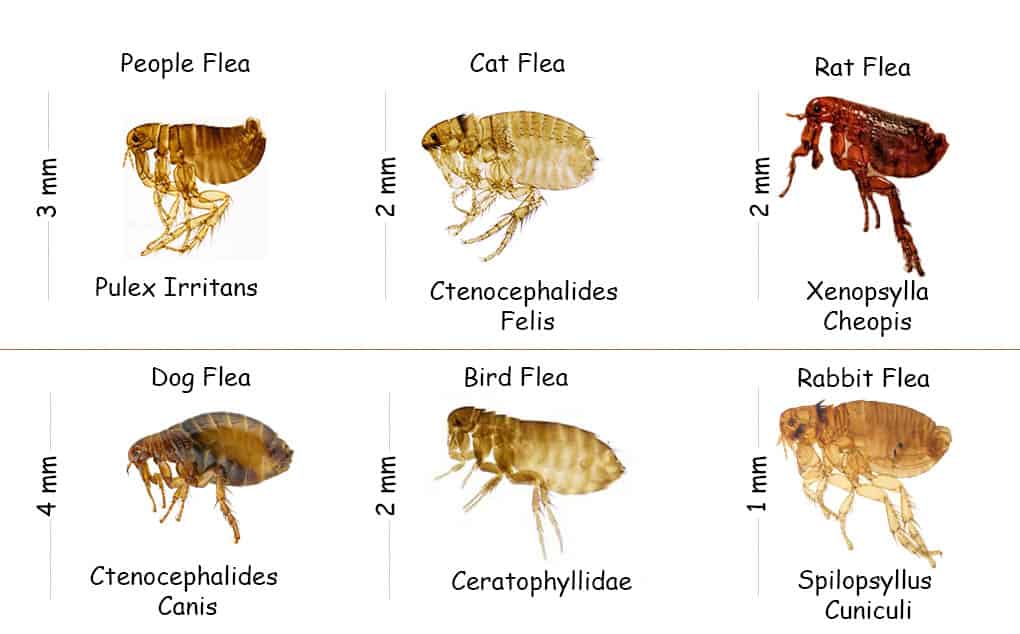
How to Identify Tiny Baby Fleas
Identifying tiny baby fleas can be challenging due to their small size and translucent appearance. However, there are several signs to look out for:
- Small, white worm-like creatures in pet bedding or carpets.
- Flea dirt (black specks) in areas frequented by pets.
- Increased scratching or discomfort in pets.
- Visible eggs or larvae in dark, undisturbed areas of your home.
Regular inspection of your pet's environment and grooming routines can help detect these pests early.
Impact of Tiny Baby Fleas
Tiny baby fleas may not bite directly, but they contribute significantly to flea infestations. Their rapid reproduction and ability to survive in various environments make them a persistent threat. Here are some impacts:
Health Risks
Fleas can transmit diseases such as flea-borne typhus and tapeworms. They can also cause allergic reactions in pets and humans, leading to skin irritation and discomfort.
Environmental Damage
Infestations can damage furniture, carpets, and other household items. The constant presence of fleas can also create a stressful environment for both pets and humans.
Preventing Tiny Baby Fleas
Prevention is the best strategy when dealing with tiny baby fleas. Here are some effective preventive measures:
- Regularly vacuum your home, especially areas where pets spend time.
- Wash pet bedding and fabrics in hot water to kill fleas and larvae.
- Use flea preventatives on pets, such as topical treatments or collars.
- Seal cracks and crevices in your home to reduce hiding spots for fleas.
Implementing these measures consistently can significantly reduce the risk of infestations.
Treatment Options
If you already have a flea problem, there are several treatment options available:
Chemical Treatments
Insect growth regulators (IGRs) and insect development inhibitors (IDIs) can effectively target flea larvae. These products disrupt the flea lifecycle, preventing larvae from developing into adults.
Natural Remedies
For those preferring natural solutions, diatomaceous earth and essential oils like lavender and eucalyptus can help control flea populations. However, it's important to use these remedies cautiously, especially around pets and children.
Environmental Control
Controlling the environment is crucial in managing flea infestations. Here are some tips:
- Keep your lawn trimmed and free of debris to reduce flea habitats.
- Regularly clean and disinfect areas where pets spend time.
- Use flea traps and monitors to detect and control infestations.
By maintaining a clean and flea-free environment, you can prevent infestations from taking hold.
Protecting Your Pets
Your pets are the primary targets of fleas, so protecting them is essential. Regular grooming and flea checks can help detect and address issues early. Additionally, consult your veterinarian for the best flea prevention products suited to your pet's needs.
Protecting Your Home
Protecting your home involves a combination of cleaning, treatment, and preventive measures. Regular vacuuming, using flea sprays, and maintaining a clean environment are all effective strategies. Consider professional pest control services if the infestation is severe.
Conclusion
Tiny baby fleas may be small, but they can cause significant problems if not addressed promptly. By understanding their lifecycle, recognizing signs of infestation, and implementing preventive measures, you can effectively manage and control flea populations. Remember to consult professionals and use trusted products for the best results.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from it. Leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions, and explore more informative articles on our website.
References: