Irritating, pungent, suffocating canadian tdg: Some oels may be expressed in units such as fibres/cc (e.g.,. The occupational hygiene is the branch of occupational health and safety which focuses on the prevention of the occupational diseases.
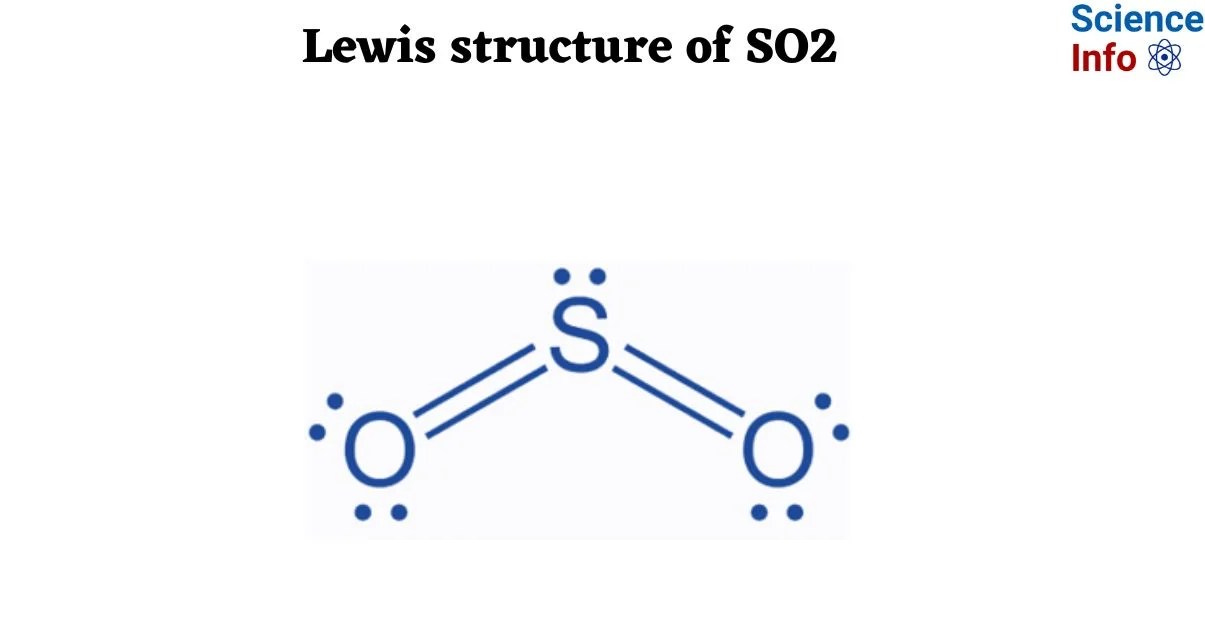
Lewis Dot Structure For So2
Welding fumes generally contain particles from the electrode and the material being welded. What does ld 50 mean? However, in most cases, the exposure levels and exposure durations are unknown or crudely estimated.
The employer must make sure that a hazard assessment is performed before workers enter a confined space.
Welding fumes are a complex mixture of metals metallic oxides, silicates, and fluorides. Back to top ld stands for lethal dose. Welding fumes are a complex mixture of metals metallic oxides, silicates, and fluorides. It poses a very serious inhalation hazard.
When can i convert mg/m3 to ppm? What are other names or identifying information for sulfur dioxide? Sulphur dioxide, so2, sulfur oxide, sulfurous oxide g processes, in food proces odour: Occupational exposure limits (oels, threshold limit values (tlvs), permissible exposure levels (pels), etc.
Ld 50 is the amount of a material, given all at once, which causes the death of 50% (one half) of a group of test animals.
There is a large amount of information on human exposures. This state is the reason exposure limits are usually expressed in mg/m3. Toxicologists can use many kinds of animals but most often testing is done with. What are other names or identifying information for sulfur dioxide?
What personal protective equipment (ppe) is needed when working with sulfur dioxide? Effects at various exposure levels are believed to be as follows: What must the employer do when atmospheric testing is needed for a confined space? Hydrogen sulfide (h2s) is a very toxic gas at normal temperatures.

Occupational exposure limits (oels, threshold limit values (tlvs), permissible exposure levels (pels), etc.) can be expressed in parts per million (ppm) only if the substance exists as a gas or vapour at normal room temperature and pressure.
Fumes are formed when a metal is heated above its boiling point and its vapours condense into very fine, particles (solid particulates).
